Shell Programming
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello world!"pid=`ps -e | grep crond | awk '{print $1}'`
kill -9 $pid유용한 툴
- vi
- gedit
- awk
- sed
Troble Shooting
도구
- 프로세스 디버깅 도구 : ps/pgrep/pstree/top
- 시스템콜(system call) 추적 도구 : strace
- 프로세스의 역추적 : 마법키? 사용
- 오픈파일 확인 도구 : lsof
프로세스 상태

http://www.makelinux.net/books/lkd2/ch03lev1sec1
pid_max
man procProcess State Codes
man ps좀비 프로세스 확인 및 처리
ps -el좀비프로세스 확인
ps-el | awk '$2=="Z" { print $5 }'zombie.sh
#!/bin/bash
# check the zombie process
ppid=`ps -el | awk '$2=="Z" {print $5}'`
for pid in $ppid
do
ps -e | grep $pid
donethread 조회
gcc countThead.c -o countThread -lpthread
ps -eL | grep countThread
ps -eLo "pcpu,rss,vsz,command" | grep countThread
ps -eo "pid,ppid,rss,vsz,command" | grep firefoxProcess monitoring
#!/bin/bash
#Monitoring processes
if [ $# -ne 1 ]
then
echo "Usage : $0 process_name"
exit 1
fi
while true
do
ps -eo "pid,ppid,rss,vsz,command" | grep $1 | grep -v grep
sleep 3
donepgrep, pstree, top
strace
파일로 결과 저장
strace -o /tmp/id.strace id파일에 관련된 것만 출력
strace -e trace=file id프로세스에 관련된 것만 출력
strace -e trace=process idtelnet 설치
yum install -y telnetd
service xinetd restart
yum install -y telnet
strace -p `pgrep xinetd`
strace -p `pgrep xinetd` -f -e trace=network좋은데 결과를 읽기가 너무 힘들다 ㅠㅠ
- 참고
http://chadfowler.com/blog/2014/01/26/the-magic-of-strace/
http://www.hokstad.com/5-simple-ways-to-troubleshoot-using-strace
- 조금더 간단한 명령 ltrace
실제 예제
fileopen 이라는 프로그램이 실행시 Permission denied가 뜬다
strace 실행
strace ./fileopen결과
open("/etc/shadow", O_RDONLY) = -1 EACCES (Permission denied)ltrace 실행
ltrace ./fileopen결과
fopen("/etc/shadow", "r") = 0
perror("fopen"fopen: Permission denied
)lsof - list open files
특정파일을 오픈하고 있는 프로세스 추적
lsof /etc/passwdftp포트가 열고있는 파일리스트
lsof -i:ftp명령 반복
lsof 0r 3 -i:telnet특정 프로세스가 오픈하고 있는 파일
lsof -p `pgrep sshd`- lsof -p 명령은 PID를 하나만 받으므로 sshd 프로세스가 여러개일경우 오류가 날 수 있다.
netstat
netstat -atp
netstat -atp | grep telnetp 옵션 강추. 프로세스 정보도 함께 보여줌
ifconfig
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST 올라와있고 broadcast 가능하며 실행되고 있고 multicast가능
- eth+숫자 : 외부와 통신
- lo : loopback
- ::1/128 -> ipv6 앞부분이 모두 00인 경우 표기법
- /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth? 네트웍설정
Gateway 확인
routeor
netstat -rARP
OSI 1, 2계층에서는 mac addr을 사용하여 통신함
arp 테이블에서 IP와 mac addr을 매핑해둔다
tcpdump
tcpdump -i lo -w /tmp/tcpdump.log
tcpdump -r /tmp/tcpdump.log port telnetwireshark
yum install wireshark-gnomelo 살리기
ifup loLinux Filesystem

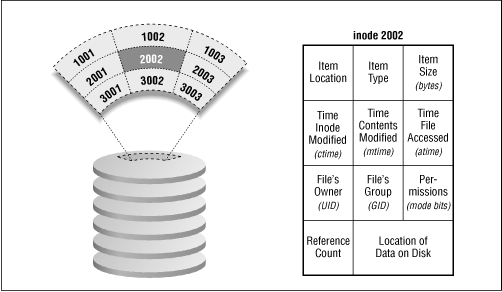
history
ext2 -> ext3 (journaling) -> ext4 (journal checksum, delayed file space allocation)
http://www.linuxdevelopernews.com/a-brief-history-of-ext2-ext3-and-ext4-2011-12
xfs, brfs(Btree Filesystem)
## 참고 http://egaoneko.github.io/os/2015/05/24/linux-starter-guide-4.html
e2fsck
[root@localhost VMware Tools]# umount /data
[root@localhost VMware Tools]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 18143556 5160340 12054912 30% /
tmpfs 1958420 224 1958196 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 289293 74645 199288 28% /boot
.host:/ 104318044 71775404 32542640 69% /mnt/hgfs
/dev/sr0 71618 71618 0 100% /media/VMware Tools
[root@localhost VMware Tools]#
[root@localhost VMware Tools]# e2fsck /dev/sdb1
e2fsck 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
/dev/sdb1: clean, 11/327680 files, 55935/1309289 blocks
[root@localhost VMware Tools]# e2fsck -f /dev/sdb1
e2fsck 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes
Pass 2: Checking directory structure
Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity
Pass 4: Checking reference counts
Pass 5: Checking group summary information
/dev/sdb1: 11/327680 files (0.0% non-contiguous), 55935/1309289 blocks
[root@localhost VMware Tools]#mke2fs 를 이용한 superblock backup확인
mke2fs /dev/sdb1 --날라감 포맷명령
[root@localhost VMware Tools]# mke2fs -n /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
327680 inodes, 1309289 blocks
65464 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280
40 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
[root@localhost VMware Tools]#tune2fs
ext2 -> ext3 인 경우 journaling 추가
tune2fs -j 장치명
ext3 -> ext4
[root@localhost ~]# mount
/dev/sda2 on / type ext4 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,rootcontext="system_u:object_r:tmpfs_t:s0")
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext4 (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
.host:/ on /mnt/hgfs type vmhgfs (rw,ttl=1)
vmware-vmblock on /var/run/vmblock-fuse type fuse.vmware-vmblock (rw,nosuid,nodev,default_permissions,allow_other)
gvfs-fuse-daemon on /root/.gvfs type fuse.gvfs-fuse-daemon (rw,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/sr0 on /media/VMware Tools type iso9660 (ro,nosuid,nodev,uhelper=udisks,uid=0,gid=0,iocharset=utf8,mode=0400,dmode=0500)
/dev/sdb1 on /data type ext3 (rw)
[root@localhost ~]#tune2fs -O extents,uninit_bg,dir_index /dev/sdb1
# e2fsck /dev/sdb1
mount /data –오류! cat /etc/fstab에 정의된 fs타입과 다름
mount /dev/sdb1 /data
[root@localhost ~]# mount
/dev/sda2 on / type ext4 (rw)
proc on /proc type proc (rw)
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,gid=5,mode=620)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,rootcontext="system_u:object_r:tmpfs_t:s0")
/dev/sda1 on /boot type ext4 (rw)
none on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type binfmt_misc (rw)
.host:/ on /mnt/hgfs type vmhgfs (rw,ttl=1)
vmware-vmblock on /var/run/vmblock-fuse type fuse.vmware-vmblock (rw,nosuid,nodev,default_permissions,allow_other)
gvfs-fuse-daemon on /root/.gvfs type fuse.gvfs-fuse-daemon (rw,nosuid,nodev)
/dev/sr0 on /media/VMware Tools type iso9660 (ro,nosuid,nodev,uhelper=udisks,uid=0,gid=0,iocharset=utf8,mode=0400,dmode=0500)
/dev/sdb1 on /data type ext4 (rw)참고 To enable the ext4 features on an existing ext3 filesystem, use the command: # tune2fs -O extents,uninit_bg,dir_index /dev/DEV WARNING: Once you run this command, the filesystem will no longer be mountable using the ext3 filesystem! After running this command (specifically, after setting the uninit_bg parameter), you MUST run fsck to fix up some on-disk structures that tune2fs has modified: # e2fsck -fDC0 /dev/DEV
https://ext4.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Ext4_Howto#Converting_an_ext3_filesystem_to_ext4
시스템 튜닝 데몬 tuned
참고
[root@localhost tune-profiles]# pwd
/etc/tune-profiles
[root@localhost tune-profiles]# ls
active-profile laptop-ac-powersave throughput-performance
default laptop-battery-powersave virtual-guest
desktop-powersave latency-performance virtual-host
enterprise-storage server-powersave
functions spindown-disk커널파라미터 확인
sysctl -a프로파일 변경
[root@localhost tune-profiles]# tuned-adm profile enterprise-storage
Switching to profile 'enterprise-storage'
Applying deadline elevator: sda sdb sdc [ OK ]
Applying ktune sysctl settings:
/etc/ktune.d/tunedadm.conf: [ OK ]
Calling '/etc/ktune.d/tunedadm.sh start': [ OK ]
Applying sysctl settings from /etc/sysctl.conf
Starting tuned: [ OK ]
[root@localhost tune-profiles]# tuned-adm active
Current active profile: enterprise-storage
Service tuned: enabled, running
Service ktune: enabled, running
[root@localhost tune-profiles]#부팅시 문제

RHEL6 vs RHEL7 교재 참고
root 비밀번호 잊어버렸을때
- 부팅시 runlevel 1로 변경 후 재부팅하면 비번없이 로그인됨 (RHEL6의 경우)
- passwd root 로 비번 재설정
파일시스템 마운트 실패시
/etc/fstab
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Tue Aug 25 01:29:29 2015
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=807ea5cc-3c92-4a88-be4d-2630553640af / ext4 defaults 1 1
UUID=71e68e21-ea8c-4a16-a71d-85e0e03789a8 /boot ext4 defaults 1 2
UUID=fdff50ba-06c8-4548-a803-2a9e02aebbeb swap swap defaults 0 0
tmpfs /dev/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
UUID="06770c0a-8b83-43ab-be41-f53be632e42b" /data ext3 defaults 1 3[root@localhost ~]# blkid /dev/sdb1
/dev/sdb1: UUID="06770c0a-8b83-43ab-be41-f53be632e42b" TYPE="ext4"- 파일시스템 마운트 실패시 파일시스템이 읽기전용으로 마운트됨
- 파일시스템을 쓰기가능한 상태로 다시 마운트
mount -o remount,rw //sbin/init이 깨졌을때
부팅시 init=/bin/bash로 재부팅
rpm -qf /sbin/init로 패키지 확인후 복구
커널 문제 추적
디바이스 드라이버는 커널에 적재되어 실행됨
커널 메시지 확인 명령
dmesg리눅스 커널 빌드
make oldconfig/menuconfig/xconfig
make
make installKernel Panic, oops, 세그멘테이션 오류(segmentation fault)
Kernel Panic

Kernel oops
kdb를 이용한 커널 디버깅
@_@;;
Kernel 덤프
dump 도구
- diskdump
- kdump (기본)
- LKCD
분석 도구
- crash
kdump 설정
- /boot/grub/grub.conf 수정 - crashkernel=128M@16M
chkconfig kdump on
service kdump start
service kdump status- 런레별별 서비스 시작여부 확인
chkconfig --list kdump- 현재 런레벨
runlevelcrash로 분석
- vmlinx 파일 위치 확인
find / -name vmlinux- crash 명령
crash vmlinux /var/crash/127.0.0.1-2015-08-27-21:57:03/vmcorecrash> set 1
PID: 1
COMMAND: "init"
crash> ascii 0x41424344
41424344: DCBA- bt [option][PID]
bt -l커널소스파일 및 라인번호 정보
live 커널 디버깅
crash vmlinux모듈
/lib/modules/uname -r/kernel/drivers/ 하위에 *.ko
insmod modulename
modprobe slip
insmod oops.ko -> crash시스템 보안
서비스 시작 설정
ntsysv
chkconfig --list
chkconfig --list xinetd
chkconfig --level 3 xinetd off
chkconfig xinetd off포트 관련
netstat -atp
lsof -i:smtpPAM
- 설정화일: /etc/pam.d/
- 모듈위치: /lib/security/ 혹은 /lib64/security/
- pam_nologin.so모듈 설정예
touch /etc/nologinulimit
- ctrl + \ 로 core 파일 떨어짐
ulimit -c unlimited- core파일 안떨어짐
ulimit -c 0파일사용권한 타그룹 권한 t
-rwsr-sr-t
- s : set uid 누가 실행하든 만든 사용자의 사용자아이디로 설정함
- s : set gid 누가 실행하든 만든 사용자의 그룹아이디로 설정함
-
t : sticky 디렉토리 권한, 타사용자가 생성한 파일 삭제 안됨
- setuid 파일 검색
find / -perm -2000- setgid 파일 검색
find / -perm -4000파일속성
- a : append만 가능
- i : immutable 추가,변경,삭제 불가
lsattr /etc/passwd
chattr +i /etc/passwd
chattr -i /etc/passwd커널 파라미터
- 기본사용법
sysctl -a | grep file-max
fs.file-max = 385767
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
385767- 수정
/etc/sysctl.conf 수정
- sysctl.conf 즉시적용
sysctl -p네트워크 보안
TCP Wrapper
-
설정화일 위치
/etc/hosts.deny
/etc/hosts.allow
-
man 참조
man hosts.deny
man hosts.allow방화벽
- 방화벽 설정 확인
iptables -L- 설정
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 --dport 80 -j REJECT- 삭제
iptables -D INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 --dport 80 -j REJECT*
iptables -P INPUT DROP